A new study unveils the existence of traveling waves of the neurochemical acetylcholine in the striatum, a region of the brain responsible for motivating actions and habitual behaviors.
Researchers have conducted a study aimed at better understanding the patterns in neural network communication associated with ‘bad’ decisions made while gambling. Their paper, published in Frontiers in Neuroscience, shows that different types of ‘bad’ decisions made while gambling, namely avoidant and approach decisions, are associated with distinct neural communication patterns.
What determines how a teenager’s brain is structured and how it evolves? Researchers have established a close link between brain activity and a maturation process called cortical thinning.
Researchers have found COVID-19 does not appear to cause direct brain damage or viral invasion. In blood or cerebrospinal fluid samples, no abnormal biomarkers were found. The findings thus suggest that post-COVID condition is not the result of ongoing infection, immune activation, or brain damage.
A recent study finds differences in functional brain connectivity in people with and without psychosis and schizophrenia that could help researchers understand the neural underpinnings of this disease.
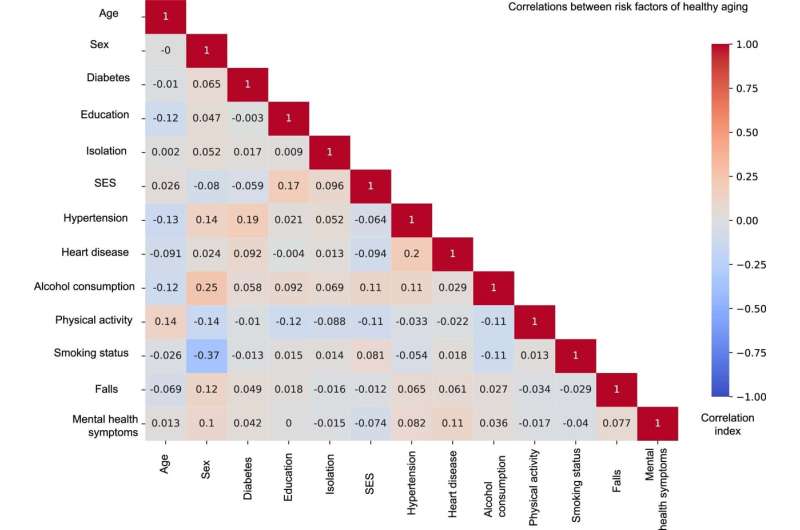
Brain health in people over age 50 deteriorated more rapidly during the pandemic, even if they didn’t have COVID-19, according to major new research linking the pandemic to sustained cognitive decline. The cognitive decline seems to have been exacerbated by several factors during the pandemic, including an increase in loneliness and depression, a decrease in exercise, and higher alcohol consumption.
Prenatal lead exposure is associated with an increased risk for cognitive developmental delay in children, according to a new study.
Children who are too short for their age can suffer reduced cognitive ability arising from differences in brain function as early as six months of age, according to new research. Stunted growth had previously been linked with poor cognitive outcomes later in life, but this is the first time that this association has been found in infancy. It is also the first time stunted growth has been linked to functional differences in how the brain works in early development.
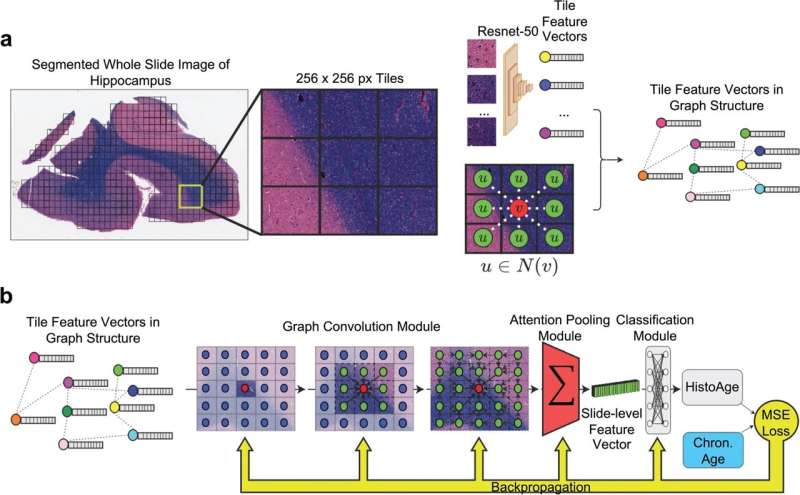
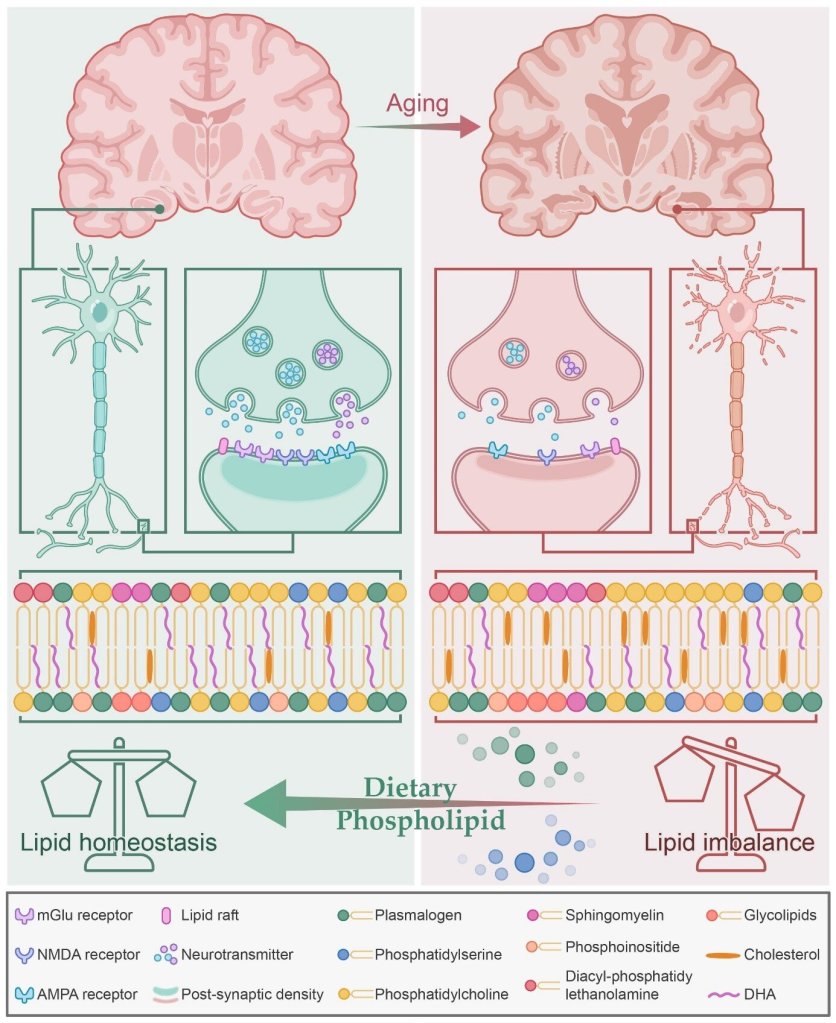
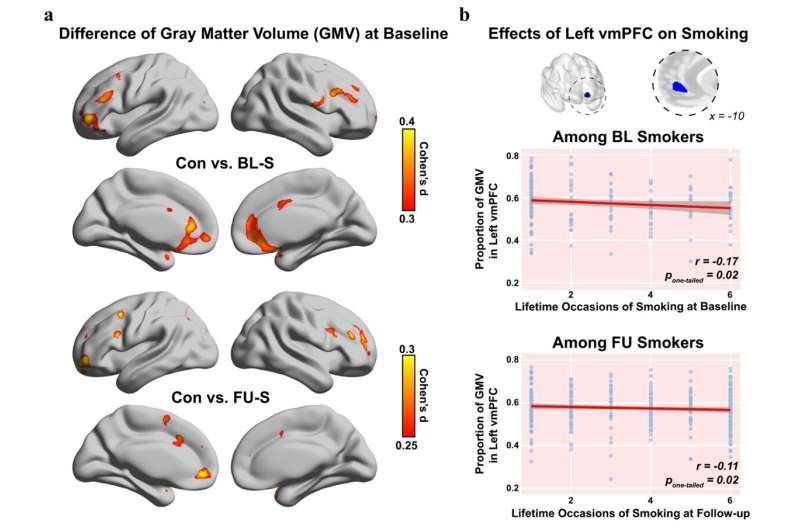
Finally this week, researchers have developed a new method for mapping how the parts of the brain “speak” to each other, critical to understanding behavior changes in patients with neurological disease.